Table Of Content
In summary, the formation of placodes in response to the first dermal signal involves activation of EDA/EDAR signaling in the epithelium, followed by epithelial WNT signaling, and subsequent activation of BMP signaling. The actions of EDA/EDAR and WNT promote placode formation, whereas BMP signaling represses placode fate in adjacent skin [6]. Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing. When taking history in a patient with hair loss, it is imperative to determine what the patient is experiencing.
How Do Hair Follicles Function?
''Grey's Anatomy'': George's bad hair day - Entertainment Weekly News
''Grey's Anatomy'': George's bad hair day.
Posted: Mon, 15 Jan 2007 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Activation of this β-catenin pathway seems to be essential for the epithelial ability of the hair follicle production [7]. In utero, type and distribution of each hair follicle over the entire body are determined. The genes that are expressed before the signs of hair follicle formation constitute the precise spacing and distribution of the follicles.
Camilla Luddington Debuts New Blonde Hair Ahead of 'Grey's Anatomy' Season 18 – See the Pic! - Just Jared
Camilla Luddington Debuts New Blonde Hair Ahead of 'Grey's Anatomy' Season 18 – See the Pic!.
Posted: Sat, 18 Sep 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Outer root sheath
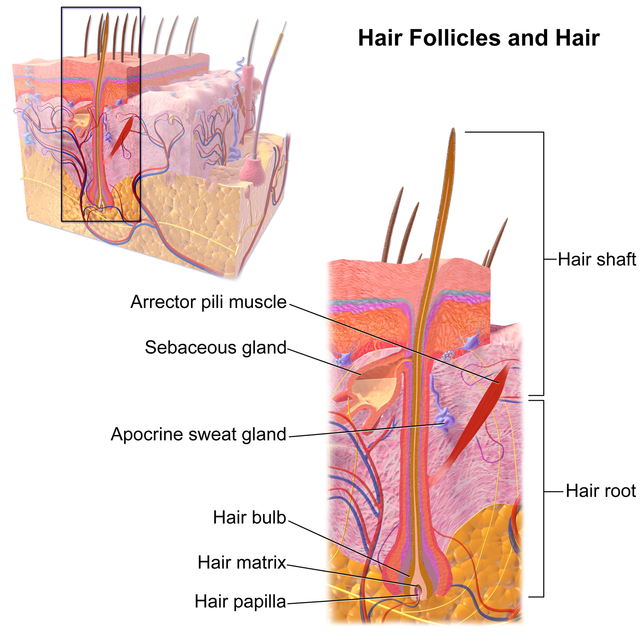
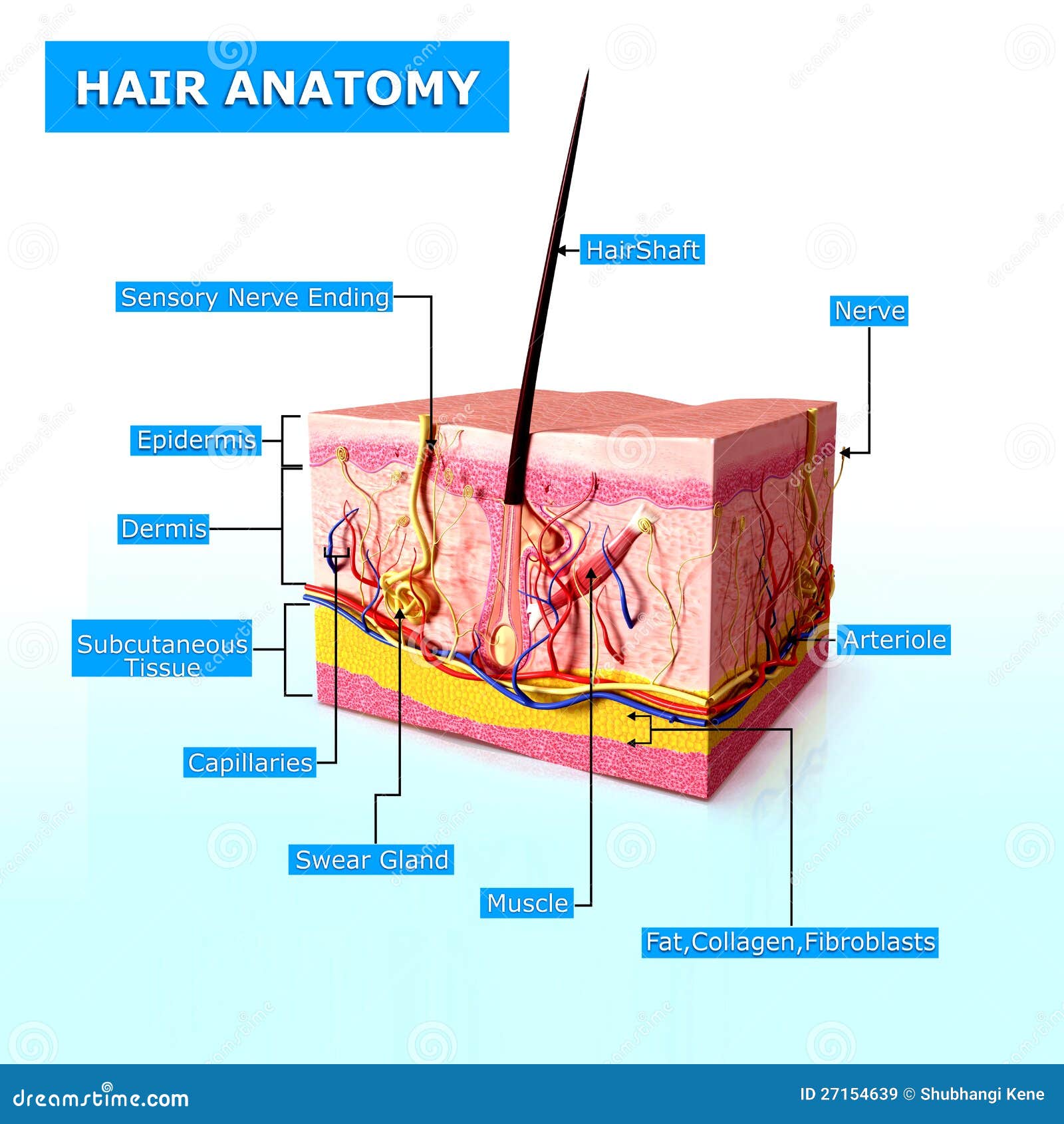
The hair shaft is the part of the hair not anchored to the follicle, and much of this is exposed at the skin’s surface. The rest of the hair, which is anchored in the follicle, lies below the surface of the skin and is referred to as the hair root. The hair root ends deep in the dermis at the hair bulb, and includes a layer of mitotically active basal cells called the hair matrix. The hair bulb surrounds the hair papilla, which is made of connective tissue and contains blood capillaries and nerve endings from the dermis (Figure 1). Hair follicle melanocytes and their precursors reside in the hair matrix and along the outer root sheath of anagen hair follicles. However, production of hair pigment (black eumelanin and/or the reddish pheomelanin) only occurs in the specialized hair follicle pigmentary unit, located above and around the dermal papilla during anagen III–VI.
Do hair follicles heal after an injury and will my hair grow back?
They eventually shed by about 36 to 40 weeks gestation and are replaced by vellus hairs that cover most areas of the body. Meanwhile, thicker, courser terminal hairs can be found on the head in certain areas such as the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Beard hairs will arise once puberty is reached, with androgen hormones transforming the vellus hairs in this area into terminal hairs.
4, these signals were observed in the X-ray data in all specimen and assigned to the coiled-coil protein phase. We note that these peaks are related to generic α-helical coil structures of monomeric proteins, and not specific to a certain type of protein. The hair strands were oriented in the X-ray diffractometer with their long axis along qz. Two-dimensional X-ray data were measured for each specimen covering distances from about 3–90 Å including signals from the coiled-coil α-keratin phase, the intermediate fibrils in the cortex and from the cell membrane complex. The 2-dimensional data were integrated and converted into line scans and fit for a quantitative analysis. There is less interest for the mechanism of the hair shedding but from the patient’s perspective it is probably the most important part of the hair growth.
Structure of Hair
The series premiered on March 27, 2005, on ABC as a mid-season replacement. 7B between father and daughter also enables the study of the effect of hair care products, such as shampoo and conditioner on the molecular structure of hair. While Subject 2 (father) uses soap and shower gel to clean scalp and hair, Subject 1 (daughter) regularly uses shampoo and conditioner. The identical X-ray signals indicate that these products do not have an effect on the molecular structure of keratin and membranes deep inside the hair (within the resolution of our experiment). The first sign of catagen is the termination of melanogenesis in the hair bulb. Follicular epithelium, mesenchyme, neuroectodermal cell populations and also perifollicular vascular and neural systems demonstrates cyclic changes in differentiation and apoptosis.
3. Molecular structure
She is currently located in East Los Angeles, and lives in a charming one-bedroom guesthouse with her dog, a 12-lb spaniel mix named Holly. After a makeup artist helped Vanessa select her first foundation at age 16, she was hooked. She began pursuing her passion in 2005 by working at a makeup counter, but found her true calling when Jenny asked her to join Blushing Beauty in 2014. Outside of her work in the makeup industry, Vanessa also makes jewelry with natural stones, spends as much time as possible outdoors, and hangs out with her two adorable pups, Lola and Robin. Oh, and she absolutely loves sweets (but, c’mon, who doesn’t??).
Hair and Scalp Disorders
These cortical cells were found to be approximately 1–6 µm in diameter and 50–100 µm in length (Randebrook, 1964). In wool fibres as well as human hair, the cortical cells were observed to be divided into different regions termed orthocortex, paracortex and mesocortex (Mercer, 1953). The difference in distribution of these cell types is an important factor for determining the curvature of the hair fibre (Kajiura et al., 2006).
Hair bulb
Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), fibroblast growth factor-7 hepatic growth factor (HGF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are thought to be important for anagen maintenance [36]. Ectodysplasin (EDA) and its receptor (EDAR) are another important pathways involved in the placode stage of hair morphogenesis. The mouse EDAR mRNA is expressed in the epithelium before placode formation, and then becomes restricted to placodes, whereas the EDA mRNA is still expressed even after placode formation [3, 6, 8].
But because new hairs are always growing and replacing them, this natural hair loss isn't noticeable. The color of the hair is determined by the amount of melanin in the hardened cells. This can vary a lot from person to person, and it changes over the course of a lifetime. The amount of melanin typically decreases as people get older, and more air gets trapped inside the hair – it then loses its color and turns white. Depending on someone’s original hair color and the number of white hairs that grow, the hair on their head then turns gray or white.
The shape and structure of these layers are, in turn, determined by the shape of the hair follicle. Hair growth begins with the production of keratinocytes by the basal cells of the hair bulb. As new cells are deposited at the hair bulb, the hair shaft is pushed through the follicle toward the surface.
This is not involved in the formation of hair and is separated from surrounding connective tissue by the glassy membrane, a form of specialised basement membrane. The layers keratinize by forming trichohyalin granules; this is unlike the hair shaft, which undergoes trichilemmal keratinization. The outermost layer of the IRS (Henle layer) keratinizes first because it is lowest in the hair follicle. The cells of the innermost layer (IRS cuticle) point downward and inward and interconnect with the cells of the hair cuticle. These 2 cuticles are completely integrated and keratinize after the Henle layer. The middle layer (Huxley layer) keratinizes after the IRS cuticle and the hair cuticle.
The details of these elements and further information regarding the epidermis can be found here. In fact, although genetic findings (Tishkoff, 2009) suggest that sub-Saharan Africans are the most genetically diverse continental group on Earth, Afro-textured hair approaches ubiquity in this region. This points to a strong, long-term selective pressure that, in stark contrast to most other regions of the genomes of sub-Saharan groups, left little room for genetic variation at the determining loci. Such a pattern, again, does not seem to support human sexual aesthetics as being the sole or primary cause of this distribution. Thin strands that sometimes are almost translucent when held up to the light.
Hair shaft pigmentation ensures multiple benefits including UV protection, thermoregulation and sexual perceptions. Furthermore, the hair pigment, melanin, is a potent free-radical scavenger. Melanin production inside the active anagen hair bulb may, therefore, help to buffer cell stress induced by reactive oxygen species. Melanin can be black, brown, or yellow, and varying combinations and quantities of each type gives us each our own unique hair color. The infundibulum is the upper portion of the hair follicle, above the entry of the sebaceous duct. Because of the abundance of AMPs, the dermal papilla stains positively with Alcian blue and metachromatically with toluidine blue.
The outer root sheath (ORS) covers the IRS as it extends upward from the matrix cells at the lower end of the hair bulb to the entrance of the sebaceous gland duct. The ORS is thinnest at the level of the bulb and thickest in the middle portion of the hair follicle. The ORS cells contain clear, vacuolated cytoplasm because of the presence of large amounts of glycogen. In darkly pigmented individuals, melanin can be found in abundance within the melanophages of the dermal papilla. The hair matrix is the actively growing portion of the follicle consisting of a collection of epidermal cells that rapidly divide, move upward, and give rise to the hair shaft and the internal root sheath. The typical mammalian hair consists of the shaft, protruding above the skin, and the root, which is sunk in a pit (follicle) beneath the skin surface.
Medullary cells contain glycogen-rich vacuoles and medullary granules, which contain citrulline (similar to the cells of the IRS). In the time of Confucius (5th century BCE), the Chinese grew out their hair and often tied it, as a symbol of filial piety. Regular hairdressing in some cultures is considered a sign of wealth or status.

No comments:
Post a Comment