
The color of your hair follicle doesn’t relate to the color of your hair. Telogen effluvium is when hair roots are pushed into the telogen resting phase. This usually occurs after some stress and can be acute or chronic. Hair has many areas of clinical significance, which include diseases of hair loss, excess, alterations due to nutritional deficiencies, infectious causes, and effects of drug reactions.
1. Hair growth cycle
Moreover the follicular papilla is an essential source of growth factors [1, 3, 16, 28]. The main component of the cortex is a keratin coiled-coil protein phase. The proteins form intermediate filaments, which then organize into larger and larger fibres. The common features observed in the X-ray data of all specimens are signals related to the coiled-coil keratin phase and the formation of intermediate filaments in the cortex, and the cell membrane complex. Signal assignment and corresponding length scales are shown in the figure.
Scalp histology
An abnormal signal was previously reported by James et al. (1999) in hair samples of patients with breast cancer. Such an approach is quite intriguing, as scanning of hair samples could be used as easy, inexpensive and non-invasive screening techniques in the diagnosis of cancer. James et al. (1999) observed a ring-like signal at 44.4 Å, at the position of the lamellar plasma membrane signal, and assigned this signal to the presence of breast cancer. The analysis and assignment was questioned later on by Briki et al. (1999) and Howell et al. (2000), who observed this feature in healthy and cancer patients in equal measure. The ring-like 45 Å signal is also present in the data for all individuals included in our study, such that a relation to breast cancer can most likely be excluded.
Discovery of hair structure 'critical' for cosmetics industry's understanding - CosmeticsDesign-Europe.com
Discovery of hair structure 'critical' for cosmetics industry's understanding.
Posted: Thu, 30 Jul 2015 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Main cast
Dr. Herman selects Robbins for a fetal surgery fellowship and becomes her mentor. Differences in the X-ray data between individuals were observed in the wide angle region (WAXS) of the 2-dimensional data in Fig. Figure 7A shows a comparison between individual 3 and 4 to illustrate the effect. For an easy comparison, the original data were cut in half and recombined, such that the left half depicts individual 3, and the right half individual 4. The keratin proteins in the cortex are known to organize in bundles whose structures are dominated by α-helical coiled-coils (Pauling & Corey, 1950; Pinto et al., 2014; Yang et al., 2014).
Scalp
Tightly coiled hair in its natural state may be worn in an Afro. This hairstyle was once worn among African Americans as a symbol of racial pride. African Americans as a whole have a variety of hair textures, as they are not an ethnically homogeneous group, but an ad-hoc of different racial admixtures. The eyebrows provide moderate protection to the eyes from dirt, sweat and rain. They also play a key role in non-verbal communication by displaying emotions such as sadness, anger, surprise and excitement.
Human hair growth
Grey's Anatomy star unveils dramatic hair transformation ahead of season 18 - HELLO!
Grey's Anatomy star unveils dramatic hair transformation ahead of season 18.
Posted: Thu, 16 Sep 2021 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Eumelanin is the dominant pigment in brown hair and black hair, while pheomelanin is dominant in red hair. Blond hair is the result of having little pigmentation in the hair strand. Above the dermal papilla is the hair matrix which consists of proliferating keratinocytes. These cells proliferate and gradually move upwards where they are keratinized to produce the hair shaft. The hair bulb comprises the expanded portion of the inferior hair follicle and contains the dermal papilla and hair matrix. It’s in the shape of a cylinder with a rounded bottom in your skin.
Hair loss can refer to increased daily hair loss, which a clinician will elicit by asking if the patient notices more hair on his or her pillow or more hair in the shower after bathing. Hair loss can also refer to apparent hairlessness, which a clinician will elicit by asking if the patient notices areas without hair or regions where hair seems to be less thick or provide less coverage. Teasing out this distinction is necessary to determine the correct diagnosis. The loose areolar tissue forms a loose connection between the epicranial aponeurosis and the pericranium.
Glossy (vitreous) layer
Lineage studies have proven that bulge cells are multipotent and that their progeny generate the new lower anagen hair follicle [21]. One of the most distinguishing features of stem cells is their slow-cycling nature, presumably to conserve their proliferative potential and to minimize DNA errors that could occur during replication. On entering the hair bulb matrix, they proliferate and undergo terminal differentiation to form the hair shaft and inner root sheath. They also migrate distally to form sebaceous glands and to proliferate in response to wounding [16, 20, 22]. They are tubular and are formed from multiple layers of epithelial cells.
Microanatomy of Catagen Phase Hair
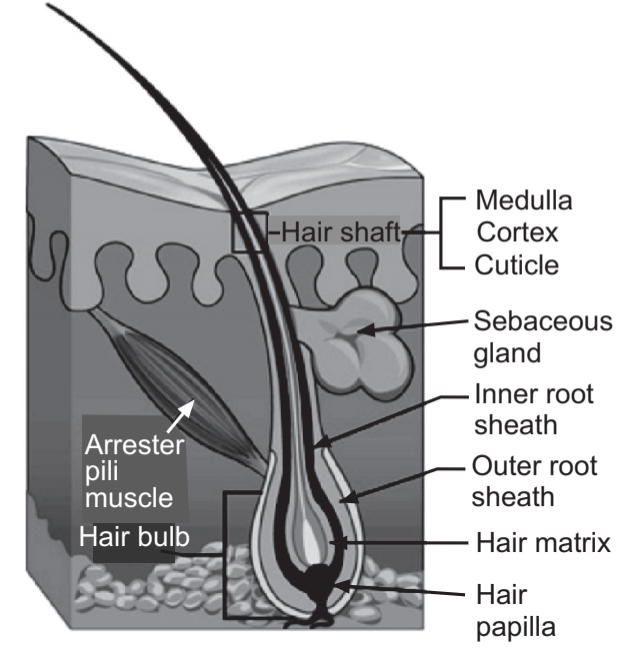
The hairs of the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes are of separate types from these others and develop fairly early in life. On the scalp, where hair is usually densest and longest, the average total number of hairs is between 100,000 and 150,000. Human hair grows at a rate of about 0.5 inch (13 mm) per month.
The upper layers of the scalp can slide over the connective tissue beneath them, which is why the skin on your head has some ‘movement’. The suprabulb region extends from the hair bulb to the isthmus and consists of components of the hair shaft, IRS, ORS, vitreous layer, and fibrous root sheath. Although vellus hairs greatly outnumber terminal hairs, the latter are more important. Therefore, the discussion of hair anatomy in this article focuses on terminal hairs.
The follicle remains in this stage until the hair germ which is responsive to anagen initiating signals from the dermal papilla, starts to show enhanced proliferative and transcriptional activity in late telogen, leading to the initiation of anagen [2, 39]. Several molecular pathways, growth factors, proteins and genes play substantial roles for the development of the hair follicle. Canonical (β-catenin dependent) WNT (wingless-type integration site) signals are candidates for the initial dermal message, and it is believed that they precede other activators and regulators of appendage development.
While the two specimens both show the general features, differences are observed in the region of signal from the cell membrane complex. (B) Comparison between individuals 1 and 2, father and daughter. The data in (C) (individuals 9 and 12) are from identical twins. Data in (D) was taken from fraternal twins (individuals 10 and 11). While different individuals in general show different membrane patterns (A), features in (B) and (C) perfectly agree. Fraternal twins show slight differences in their pattern in (D).
Enhanced knowledge on the normal dynamics of the hair provides understanding the basis of how the follicle behaves during a disease. However recent progress in our understanding of the biology and pathology of hair follicles should lead more effective therapies for hair disorders. Medulla is located in the center of the hair shaft preferably presented in coarser fibers. The hair medulla contains structural proteins that are markedly different from other hair keratins and eosinophilic granules that are filled by an amino acid, citrulline and eventually form internal coatings within the membranes of mature cells [14, 16, 17].

No comments:
Post a Comment